In this blog series we will explore Remote telemonitoring in people using CPAP/APAP therapy to treat sleep Apnoea syndrome and the benefit’s for patient’s, Healthcare Services, Policy Makers and the Environment.
Introduction: Sleep apnoea is a common sleep disorder that is estimated to affect 963 million adults between the ages 30-69 years globally and in the UK the prevalence of OSA is estimated to be 24.5% (1). This is a staggering number that poses many clinically significant challenges for health care providers in the National Health Service with consequences for cardiovascular health, cerebrovascular health, neurological health, metabolic health, including type 2 diabetes and obesity, mental well-being, quality of life, driving safety and work productivity (2). Treatment options such as Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Auto-Adjusting Positive Airway Pressure (APAP) devices are widely used. However, managing these therapies effectively can be challenging for both healthcare providers and patients.
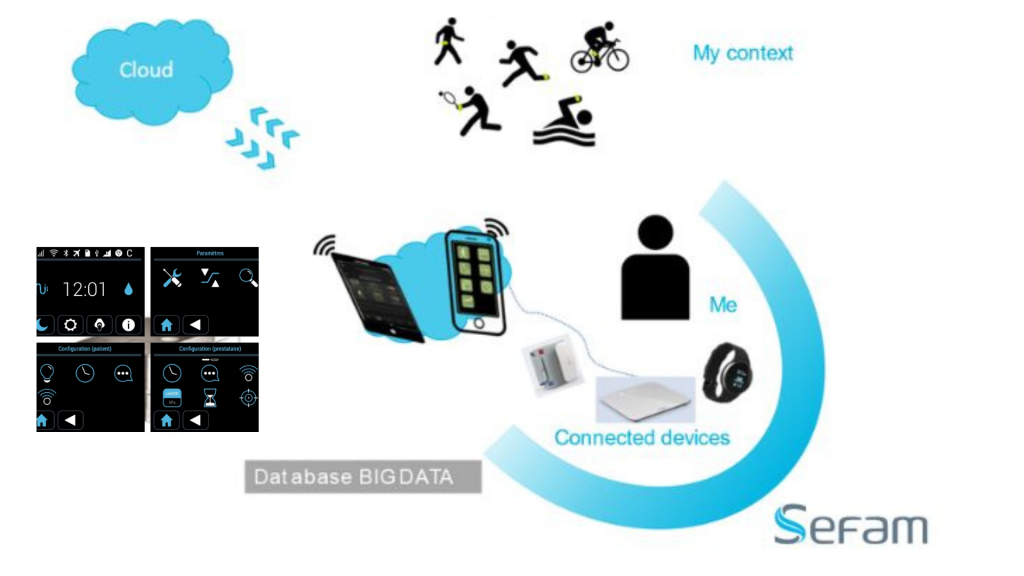
Recent innovations in CPAP software have greatly improved remote monitoring features, enabling healthcare professionals and patients to oversee therapy performance in real-time. These systems now utilise mobile phone and wireless connectivity, cloud storage, and sophisticated data analysis to track metrics like airflow, device usage, leak rates, and residual apnoea and hypopnoea occurrences remotely. This progress allows for quicker clinical responses, enhances patient compliance, and supports tailored treatment modifications without frequent in-person visits (3). Overall, these technological advances are designed to make sleep apnoea management more efficient, accessible, and personalised.
Enhanced Adherence with Remote Telemonitoring for Sleep Apnoea
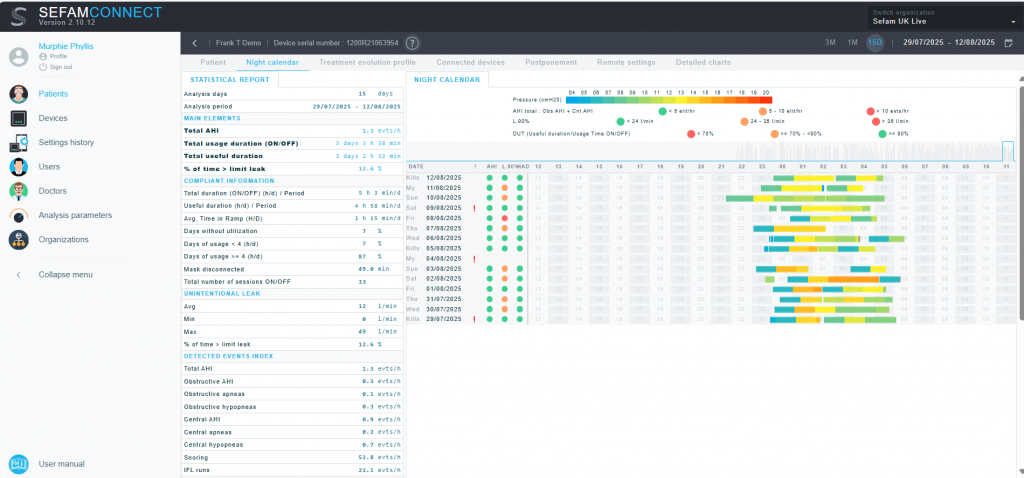
Patient adherence with CPAP or APAP therapy is the biggest challenge that patients face with this treatment option. Adherence rates long term have not changed much over the last 30 years (4). Poor adherence ranging from 30% to 60% has been reported widely (5-6). Remote telemonitoring allows sleep Medicine clinicians to remotely monitor real-time patient usage data. This data includes information on mask on time, mask fit/leakage, and treatment efficacy. With access to this data, the sleep clinician can identify adherence issues early in treatment evolution and support timely interventions, increasing the likelihood of longer-term treatment success. Several studies have now reported improved adherence to CPAP therapy with remote monitoring (7-8). A recent study by Dielesen et al 2025 has shown early follow up within 2 weeks of commencing therapy has been shown to improve adherence rates and telemonitoring data can support early review. They concluded that determining CPAP- usage behavioural pattern in week 2 identifies risk of CPAP non- adherence at month 3 and allows for customised interventions (4).
- Virtual care provided by phone or video consultations is as effective as in-person care for improving subjective sleepiness in patients with OSAHS treated with CPAP.
- This management strategy may also improve CPAP adherence without increased costs, and can be a cost-effective follow-up management strategy, particularly in cases where patients favour this approach (8-9).
- Remote telemonitoring of CPAP therapy often improves patient adherence by offering real-time feedback, support, and prompt assistance.
- This ongoing engagement helps patients resolve issues quickly, enhances comfort, and encourages continued use, leading to higher usage rates and better treatment results compared to patients without remote monitoring.
Convenience and Comfort
Remote telemonitoring for sleep apnoea is convenient for many patients, avoiding the need to travel for in-person appointments reducing travel time and related expenses and lost work productivity. Remote review can be conducted anywhere the patient has privacy to do so, even in the work environment. This convenience contributes to improved patient satisfaction and a better overall treatment experience. Patient satisfaction with remote monitoring has been reported in a number of studies with improved quality of life also reported in patients who are being remotely monitored (7,9).
Improved Treatment Efficiency and Timely Intervention
- Remote telemonitoring facilitates the timely adjustment of CPAP or APAP settings based on real-time data.
- This personalised treatment approach ensures that patients receive the most effective therapeutic settings, reducing the need for additional interventions.
- This can support both improved quality of care and quality of life for patients. Patients can receive tailored advice and support based on their actual usage data, encouraging better adherence and proper device usage.
- Sleep Medicine Clinicians receive alerts via their cloud based software monitoring platform about mask leaks, poor usage, possible device malfunctions, allowing prompt intervention before problems worsen.
- Sleep apnoea may be a progressive condition, and delays in addressing adherence or therapy issues can have consequences such as worsening symptoms and increased health risks due to other underlying heart conditions, such as high blood pressure or other cardiovascular conditions.
- Remote telemonitoring enables sleep clinicians to identify therapy issues promptly and intervene as necessary in a timely manner.
Enhanced Patient Co-management
Remote telemonitoring encourages active patient participation in their treatment plan. Patients can access their own CPAP/APAP usage data using software apps designed to support them to track their treatment progress and to gain a better understanding of the impact of their treatment on their sleep quality and overall health. This increased engagement can support better adherence to treatment recommendations (10).
Remote telemonitoring has revolutionised the management of people living with sleep apnoea in the last two decades by offering cost-effective, time-efficient, and patient-centred benefits. From improved adherence to therapy and reduced healthcare utilisation costs, the advantages of remote telemonitoring are clear to see for patients. In the next series of blogs we will explore the benefits of telemonitoring for health care providers, healthcare organisations and policy makers. As technology continues to advance at pace, we can expect even more personalised innovations in the field of sleep medicine, further enhancing the quality of care for patients living with this long-term debilitating condition. In our next blog we will explore remote monitoring in Sleep Apnoea – Advantages for Healthcare Providers.
References:
- Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis – PubMed
- Global burden of sleep-disordered breathing and its implications – PubMed
- New management pathways for follow-up of CPAP-treated sleep apnoea patients including digital medicine and multimodal telemonitoring – PubMed
- Six early CPAP-usage behavioural patterns determine peak CPAP adherence and permit tailored intervention, in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea
- Duration of positive airway pressure adherence: how much PAP is enough? | Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine
- Long term adherence to continuous positive Airway pressure in mild obstructive sleep apnea | BMC Pulmonary Medicine | Full Text
- Remote consulting with telemonitoring of continuous positive airway pressure usage data for the routine review of people with obstructive sleep apnoea hypopnoea syndrome: A systematic review – PubMed
- The Future of Telemedicine for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment: A Narrative Review
- Virtual consultations for patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: a systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed
- Patient-Centered Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review – PMC
